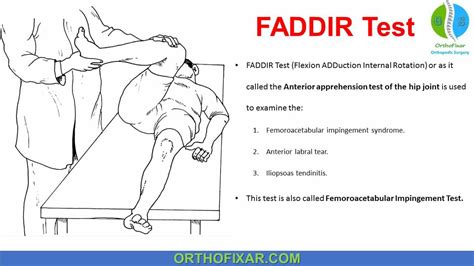
anterior hip labral tear test|labral tear physical exam tests : service The FADIR (flexion, adduction, internal rotation) test is used for the examination of femoroacetabular impingement syndrome, anterior labral tear and iliopsoas tendinitis. The premise of this test is that flexion and adduction motions approximates the .
Under the Medicare Program guidelines the coverage of sterilization is limited to necessary treatment of an illness or injury. An example of necessary treatment is the removal of a uterus or removal of diseased ovaries (bilateral oophorectomy) because of a tumor, or bilateral .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Autoclavable, UV-shielding cartridges for bioprinting. Transparent amber 3 mL cartridges for UV- and light-sensitive materials. Protective up to 550 nm wavelength. Mounted with an end and tip cap (non-autoclavable). The .
is graduated pipette more accurate than volumetric
positive fadir test meaning
The McCarthy Test is a clinical test used in the diagnosis of a hip labral tear. The shearing force-producing painful popping, clicking, or catching while performing the test indicates a possible hip labrum tear. See moreThe acetabulofemoral (hip) joint is the largest and most stable joint in the human body. The acetabular labrum is a soft-tissue structure . See moreStep 1:The patient should be lying supine with their head supported and both arms rested to their side in a comfortable position. Step 2:The . See more
positive anterior impingement test
The FADIR (flexion, adduction, internal rotation) test is used for the examination of femoroacetabular impingement syndrome, anterior labral tear and iliopsoas tendinitis. The .
The McCarthy Test is a clinical test used in the diagnosis of a hip labral tear. The shearing force-producing painful popping, clicking, or catching while performing the test indicates a possible hip labrum tear.The FADIR (flexion, adduction, internal rotation) test is used for the examination of femoroacetabular impingement syndrome, anterior labral tear and iliopsoas tendinitis. The premise of this test is that flexion and adduction motions approximates the .
Imaging scans. A hip labral tear rarely occurs by itself. In most cases, other structures within the hip joint also have injuries. X-rays are excellent at visualizing bone. They can check for arthritis and for structural problems.Anterior labral tears - the pain will generally be more consistent and is situated on the anterior hip (anterosuperior quadrant) or at the groin. They frequently occur in individuals in European countries and the United States. Posterior labral tears - are situated in the lateral region or deep in the posterior buttocks. They occur less .
Anterior hip labral tears are usually caused by repetitive movements common in sports such as ballet, golf, football or hockey. Posterior hip labral tears are usually caused by traumatic injuries such as falls, accidents or high-impact sports injuries. A hip labral tear is a traumatic tear of the acetabular labrum, mostly common seen in acetabular dysplasia, that may lead to symptoms of internal snapping hip as well hip locking with hip range of motion. Diagnosis generally requires an MR arthrogram of the hip joint in question.A healthcare provider will diagnose a hip labral tear with a physical exam and some tests. They’ll examine your hip and ask you about your symptoms. Tell your provider when you first noticed pain and other symptoms, and if any activities, movements or positions make them worse.To diagnose a hip labral tear your doctor will review your medical history, conduct a physical exam, and order one or more imaging tests. As a first step toward making a diagnosis, your doctor will ask about your symptoms including when they began and which activities aggravate them.
A hip labral tear involves the ring of cartilage (labrum) that follows the outside rim of the hip joint socket. Besides cushioning the hip joint, the labrum acts like a rubber seal or gasket to help hold the ball at the top of the thighbone securely within the hip socket.Labral tears present with anterior hip or groin pain, and less commonly buttock pain. Frequently, there are also mechanical symptoms including clicking, locking, and giving way. The most consistent physical examination finding is a positive anterior hip impingement test.The McCarthy Test is a clinical test used in the diagnosis of a hip labral tear. The shearing force-producing painful popping, clicking, or catching while performing the test indicates a possible hip labrum tear.The FADIR (flexion, adduction, internal rotation) test is used for the examination of femoroacetabular impingement syndrome, anterior labral tear and iliopsoas tendinitis. The premise of this test is that flexion and adduction motions approximates the .
Imaging scans. A hip labral tear rarely occurs by itself. In most cases, other structures within the hip joint also have injuries. X-rays are excellent at visualizing bone. They can check for arthritis and for structural problems.Anterior labral tears - the pain will generally be more consistent and is situated on the anterior hip (anterosuperior quadrant) or at the groin. They frequently occur in individuals in European countries and the United States. Posterior labral tears - are situated in the lateral region or deep in the posterior buttocks. They occur less .Anterior hip labral tears are usually caused by repetitive movements common in sports such as ballet, golf, football or hockey. Posterior hip labral tears are usually caused by traumatic injuries such as falls, accidents or high-impact sports injuries. A hip labral tear is a traumatic tear of the acetabular labrum, mostly common seen in acetabular dysplasia, that may lead to symptoms of internal snapping hip as well hip locking with hip range of motion. Diagnosis generally requires an MR arthrogram of the hip joint in question.
A healthcare provider will diagnose a hip labral tear with a physical exam and some tests. They’ll examine your hip and ask you about your symptoms. Tell your provider when you first noticed pain and other symptoms, and if any activities, movements or positions make them worse.
To diagnose a hip labral tear your doctor will review your medical history, conduct a physical exam, and order one or more imaging tests. As a first step toward making a diagnosis, your doctor will ask about your symptoms including when they began and which activities aggravate them. A hip labral tear involves the ring of cartilage (labrum) that follows the outside rim of the hip joint socket. Besides cushioning the hip joint, the labrum acts like a rubber seal or gasket to help hold the ball at the top of the thighbone securely within the hip socket.
positive anterior hip impingement test
labral tear special tests hip
is graduated pipette qualitative
is it easy hard for the elderly to use pipettes
Die DIN EN ISO 13060 unterscheidet Autoklaven in die Klassen B, S und N. Alle Sterilisationsverfahren haben die Inaktivierung aller vermehrungsfähigen Mikroorganismen als Ziel. Mit Dampfsterilisatoren der Klasse B und Klasse S .
anterior hip labral tear test|labral tear physical exam tests